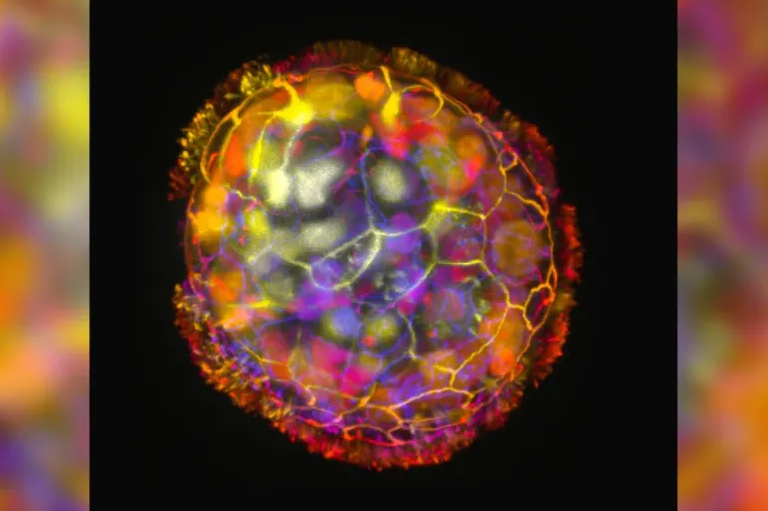
Envision a scenario where a microscopic robot, smaller than a human hair, navigates within your body, stimulating the growth of nerve cells in damaged regions. This futuristic prospect is inching closer to reality, thanks to the groundbreaking experiments conducted by scientists at Tufts University and Harvard University in the United States.
The key innovation lies in their use of human cells isolated from the trachea to create these biological robots, marking a departure from previous attempts that utilized stem cells from frog embryos to fashion “Xenobots.”
The Xenobots, crafted by researchers at the University of Vermont and other institutions, were heralded as pioneers in biotechnology. Their objective was to explore the capabilities of living cells in executing specific tasks, such as delivering targeted drugs. However, a significant hurdle impeding the practical application of these biological robots was the concern over “biological compatibility” with the human body, fearing potential immune responses.
In response, the research team led by Dr. Jizhe Gomoskaya at Tufts University introduced a novel approach, manufacturing biological robots entirely from human cells without resorting to genetic modifications.
These living creations, named “Anthrobots,” exhibited hair-like appendages resembling yellow strands and showcased the ability to propel themselves while promoting the growth of nerve cells in damaged areas, as described by Dr. Jizhe Gomoskaya. The intricate process of developing these Anthrobots commenced with obtaining a single cell from the surface of the human trachea, followed by successive steps that included cell cultivation, programming, assembly, and organization.
The scientists rigorously tested the functionality of these robots, assessing their performance in tasks, behaviors, and interactions with other materials.
Finally, the Anthrobots were subjected to diverse applications and tests, ranging from controlled laboratory experiments to evaluations within living organisms, portraying their potential in real-world scenarios. Witnessing a swarm of Anthrobots in action promises to be a captivating demonstration of this cutting-edge biotechnological achievement.
Leave a Reply